Quick Answer: Improving the sustainability of pickleball paddle manufacturing involves selecting eco-friendly raw materials, optimizing production processes like hot pressing1, cold pressing2, and thermoforming3, and implementing energy-efficient practices. This approach not only reduces the carbon footprint but also enhances product performance and durability for competitive and recreational play.
In the evolving world of sports equipment manufacturing, the challenge of balancing high-performance production with sustainability concerns is more critical than ever. For sustainability managers, procurement specialists, and technical decision-makers in sports manufacturing companies, understanding the environmental impact of different manufacturing processes is essential. This article dives deep into how the production of pickleball paddles contributes to carbon emissions and explores actionable strategies to minimize the environmental footprint while preserving product quality and performance.
Pickleball paddle production involves several stages, from raw material selection to final assembly. Carbon fiber, fiberglass, and composite materials4 are at the core of high-performance paddles but have varying impacts on the environment. Sustainability issues primarily revolve around:
- Energy consumption during production processes.
- Carbon emissions from raw materials extraction and processing.
- Waste generation and the lifecycle assessment5 of finished products.
- Supply chain emissions and logistics.
These environmental factors necessitate a thorough assessment and strategic implementation of green manufacturing practices, ensuring that sustainability and performance go hand in hand.
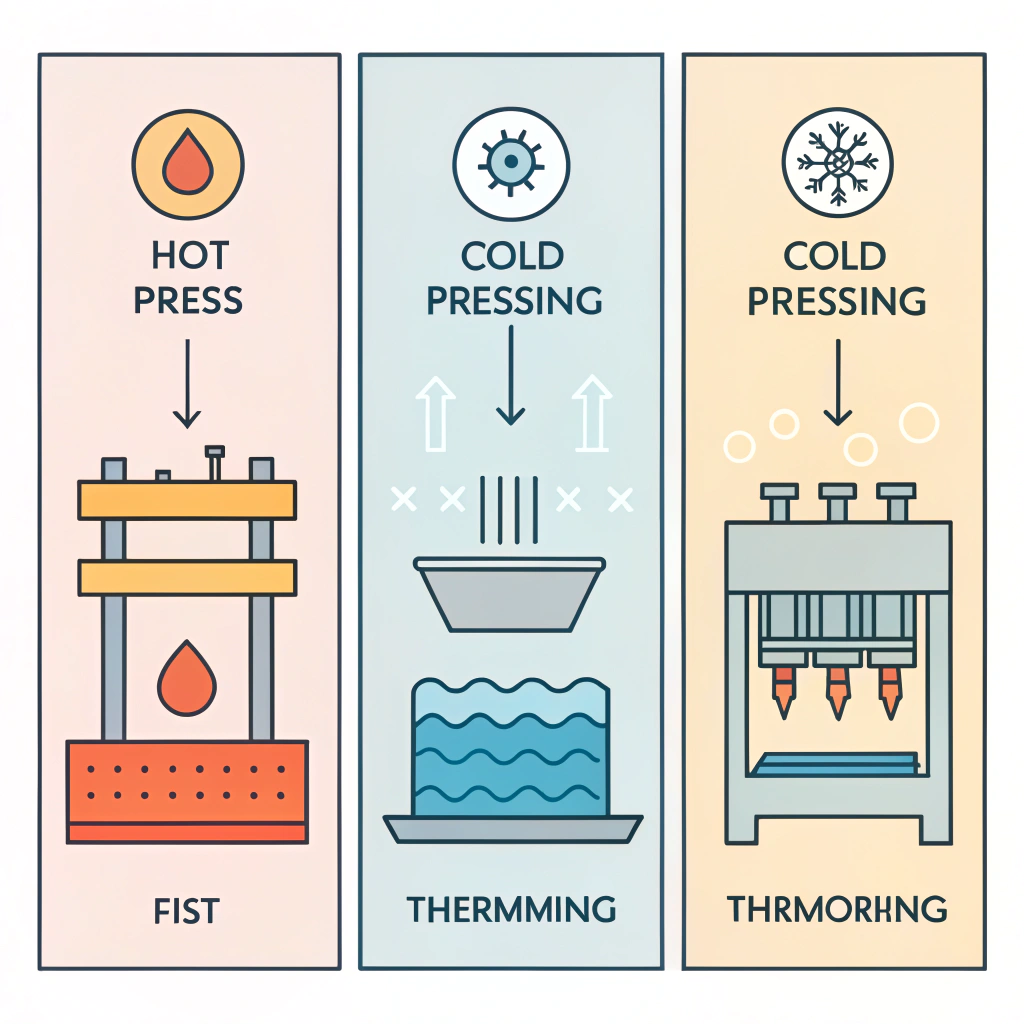
Among the critical manufacturing processes, hot pressing, cold pressing, and thermoforming each carry distinct advantages and environmental challenges. A solution-oriented approach to enhance sustainability first involves a detailed analysis of these processes.
Hot pressing uses elevated temperatures combined with pressure to shape paddle materials. This method is commonly chosen for its high production efficiency and strong end product.
Advantages:
- Fast and efficient for mass production.
- Creates high-strength paddles with excellent impact resistance.
- Improves structural integrity, suitable for competitive playing conditions.
Disadvantages from a Sustainability Perspective:
- High energy consumption due to prolonged heating phases.
- Potential alteration of material properties, which may require additional processing.
- Higher equipment costs that could translate into greater overall carbon footprint if energy sources are not renewable.
Cold pressing involves using mechanical pressure at room temperature, preserving the inherent properties of the raw materials without excessive heat.
Advantages:
- Retains the material’s natural properties, ensuring excellent ball control and flexibility.
- Lower energy requirements compared to hot pressing.
- Allows for finer control over paddle dimensions and structural precision.
Disadvantages:
- The production cycle tends to be longer, potentially increasing resource usage over time.
- Demands high-precision equipment which, if not managed efficiently, might negate some environmental benefits.
Thermoforming heats materials to a pliable state before molding them, thereby enabling complex designs and precise material distribution.
Advantages:
- Highly versatile, suitable for producing paddles with intricate design features.
- Can optimize material use, reducing wastage if properly controlled.
- Maintains the stability of the final product, enhancing performance.
Disadvantages:
- Longer production times with higher associated equipment costs.
- Energy usage is significant if the heating process is not optimized or powered by renewable energy sources.
Below is a table summarizing the key sustainability aspects of the three main production processes:
| Production Process | Energy Consumption | Material Integrity | Production Time | Environmental Impact | Cost Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hot Pressing | High | Moderate | Short | Moderate-High | High |
| Cold Pressing | Low | High | Longer | Low-Moderate | Moderate |
| Thermoforming | Moderate-High | High | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate-High |
This table offers a snapshot of how each process measures up on sustainability metrics and operational efficiency. By comparing these factors, manufacturers can identify which process—or a mix of them—best aligns with green objectives while ensuring competitive product quality.
Sustainability in pickleball paddle manufacturing is also heavily influenced by the choice of raw materials. Manufacturers like NEX Pickleball utilize a combination of high-performance materials including various types of carbon fiber, fiberglass, and composite options. Here’s how these materials weigh up in terms of environmental impact:
- 3K Carbon Fiber: Known for durability and high rebound force, but its production is energy-intensive.
- 12K Carbon Fiber: Offers superior strength and a smoother finish, however, involves higher energy usage in manufacturing.
- T300 Carbon Fiber: Balances strength with weight, making it a premium option that requires careful management of energy input during production.
While carbon fiber enhances performance, manufacturers must consider its high initial carbon footprint. Transitioning to energy-efficient processes or sourcing carbon fiber produced via greener techniques could mitigate environmental concerns.
- Fiberglass (E-Glass): Provides excellent ball control and flexibility, with a relatively lower energy cost than carbon fibers.
- Composite Materials (Carbon Fiber and Fiberglass Composite): Merges the benefits of both materials, allowing for a balance between power and control while possibly offering reduced environmental impact if optimized.
- Bamboo Core Composite and Honeycomb Cores: Present eco-friendly alternatives, as these materials can potentially lower the carbon footprint and offer enhanced shock absorption.
Integrating these materials requires an in-depth lifecycle assessment to ensure that the overall sustainability targets are met without compromising paddle quality. Advances in recycling practices and waste reduction within production cycles are promising areas for improvement.
Achieving a balance between quality manufacturing and environmental sustainability involves several proactive measures:
-
Energy Efficiency Measures:
- Implementation of renewable energy sources in the production facility.
- Upgrading to energy-efficient machinery and optimizing production cycles.
- Employing real-time energy monitoring systems to reduce wastage.
-
Sustainable Raw Material Sourcing:
- Engaging with suppliers who commit to lower-emission production methods.
- Exploring recycled or bio-based materials that offer similar performance to traditional components.
- Encouraging innovation in raw material processing to reduce energy consumption.
-
Process Optimization:
- Fine-tuning hot pressing, cold pressing, and thermoforming parameters to minimize energy usage while maintaining product integrity.
- Introducing software-driven optimization models to predict and reduce waste.
- Training operational staff in sustainable production practices to ensure consistency and reduce environmental impact.
-
Lifecycle and Waste Management:
- Conducting comprehensive lifecycle assessments to identify critical environmental hotspots.
- Implementing proper waste management systems and encouraging recycling within the production chain.
- Designing paddles that are not only high performing but also easier to recycle at the end of their life cycle.
Consider a production line that transitions from traditional hot pressing methods to a more optimized version powered by renewable energy. Such a change can reduce carbon emissions substantially. Data from similar industries show that energy-efficient equipment coupled with renewable power sources can cut energy consumption by up to 30%, while maintaining high levels of product output and quality. This transformation not only supports green initiatives but also results in cost savings over time—an essential factor for procurement specialists.
A notable example comes from a collaboration between a forward-thinking pickleball paddle manufacturer and a renewable energy provider. By integrating solar panels into their production lines for both cold pressing and thermoforming processes, the manufacturer reduced its reliance on non-renewable energy sources. They reported a 25% decrease in overall energy costs and a corresponding reduction in carbon emissions. Additionally, the use of advanced energy monitoring systems enabled them to adjust operational parameters in real-time, ensuring peak energy efficiency.
This case illustrates that with targeted investments in green technology and process optimization, manufacturers can significantly tip the scale towards greater sustainability without sacrificing production performance.
To wrap up, sustainability in pickleball paddle manufacturing is achievable through a careful balance of material selection, process optimization, and energy-efficient practices. Here are the key takeaways:
- Understand the Environmental Impact: Acknowledge how each production process and material influences the overall carbon footprint.
- Optimize Production Processes: Evaluate hot pressing, cold pressing, and thermoforming in terms of energy usage and environmental impact. Use comparative data to guide decision-making.
- Invest in Renewable Energy: Transition production facilities to renewable power sources to substantially reduce carbon emissions.
- Source Sustainably: Choose raw materials that not only meet performance standards but also come with a lower environmental cost. Consider recycled materials and bio-based alternatives.
- Monitor, Assess, and Innovate: Implement lifecycle assessments and continuous monitoring of production parameters to drive improvements and maintain sustainability standards.
Adopting these practices will not only position your manufacturing operations at the forefront of green technology but also offer a competitive advantage in markets that increasingly value environmental responsibility. For sustainability managers and procurement specialists, these actionable strategies provide a roadmap to reduce carbon footprints and support long-term business growth while meeting consumer and regulatory demands for eco-friendly products.
People Also Ask
Q: Are pickleball paddles made of carbon fiber?
A: Yes, many pickleball paddles are made with carbon fiber due to its strength, durability, and high-performance characteristics. These paddles provide excellent control and power, making them popular in competitive play.
Q: How big is the pickleball paddle market?
A: The U.S. Pickleball Paddle Market is forecasted to reach significant growth, with estimates showing a valuation of approximately USD 184.4 million in 2025 and a potential to reach around USD 368.6 million by 2034, reflecting robust market expansion at a CAGR of about 8.0%.
Q: Which pickleball paddles are not made in China?
A: Some of the pickleball paddle brands that manufacture in the US include Avoura (Encinitas, California), Engage (Oxford, Florida), Paddletek (Niles, Michigan), Players Pickleball (Ferndale, Washington), Revolin (Holland, Michigan), and certain models of Selkirk (Coeur d'Alene, Idaho).
-
hot pressing: Reading the article will provide insight into how the hot pressing process leverages heat and pressure for shaping materials, including its production efficiency and sustainability trade-offs. ↩ ↩
-
cold pressing: Reading the article will explain the cold pressing process, detailing its benefits in preserving material properties and reducing energy consumption during manufacturing. ↩ ↩
-
thermoforming: Reading the article will outline the thermoforming process, highlighting its versatility in producing complex designs and the associated energy considerations for sustainability. ↩ ↩
-
composite materials: Reading the article will help you understand the role of composite materials in achieving high performance while balancing environmental impact in manufacturing processes. ↩ ↩
-
lifecycle assessment: Reading the article will explain lifecycle assessments, detailing how they evaluate the environmental impacts from production to end-of-life, and their importance in sustainable manufacturing. ↩ ↩