Quick Answer: Lean production1 in pickleball manufacturing harnesses waste reduction, continuous improvement, and process standardization to boost productivity, quality, and cost efficiency. This article outlines the challenges unique to pickleball paddle production, analyzes root causes of inefficiencies, and recommends actionable strategies based on lean manufacturing principles.
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, lean production is more than just a buzzword—it is a proven methodology that can revolutionize the way factories operate. For manufacturers in the pickleball industry, the need is even more pronounced. With a diverse array of high-performance materials such as carbon fiber, fiberglass, and composite cores, managing production quality and efficiency becomes a formidable challenge. This article dives into how lean production methods can be adapted to streamline processes in pickleball paddle manufacturing, reduce waste, and drive operational excellence.
Lean production focuses on eliminating non-value-added activities and optimizing every step of the production process. In the context of pickleball manufacturing, this means:
• Enhancing process efficiency across different production techniques such as hot pressing, cold pressing, and thermoforming.
• Minimizing defects and inconsistencies in paddle surfaces and core materials.
• Reducing material waste, which is critical when working with premium components like 12K carbon fiber or specialized composites.
• Implementing rigorous quality control to ensure every paddle meets performance requirements.
Because pickleball paddles involve a layered sandwich composition with a honeycomb core and specialized surface materials, lean methods are essential for maintaining the delicate balance between durability, performance, and cost.
For production managers, operations directors, and process engineers, several challenges can hinder efficiency:
-
Material Variability: Different materials—whether carbon fiber variants (3K, 12K, T300), fiberglass, or composite mixtures—require tailored handling and processing. Inconsistencies in materials may lead to uneven performance or durability issues.
-
Process Complexity: The choice among hot pressing, cold pressing, or thermoforming not only affects the paddle's physical characteristics but also changes production timelines and costs. Each process has unique advantages and constraints.
-
Quality Control: Given the high-performance demands of competitive pickleball play, any lapse in quality control can result in defective paddles, increased waste, and customer dissatisfaction. Ensuring consistency across batches is a recurring challenge.
-
Waste Reduction: With expensive raw materials, even small inefficiencies lead to significant cost overruns. Lean production aims to minimize waste at every step of the manufacturing process.
-
Factory Layout and Automation: Efficient plant layout and appropriate automation are essential to minimize movement waste and optimize throughput. The design of the factory floor often plays a decisive role in production speed and safety.
Identifying the root causes of inefficiencies is the first step toward improvement. In pickleball paddle manufacturing, common sources of inefficiency include:
• Process Mismatch: Using an inappropriate production technique for a given material or design can lead to defects and increased rework.
• Inadequate Standardization: Without standardized procedures, variability creeps in during material handling and mixing, causing quality inconsistency.
• Lack of Continuous Improvement Culture: Failure to analyze and address recurring issues prevents sustainable productivity gains.
• Equipment Limitations: Insufficient investment in modern machinery and automation may result in prolonged production cycles and downtime.
Understanding these factors helps production teams implement targeted solutions and create a roadmap for continuous improvement.
Here is a comprehensive list of lean production strategies to address the challenges discussed. Each strategy is designed to optimize efficiency, reduce waste, and elevate product quality.
| Lean Production Strategy | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Value Stream Mapping2 | Visualizes each process step, identifying activities that add value versus waste. | Clear insight into bottlenecks; targeted improvement areas. |
| Standardized Work Procedures3 | Develops detailed work instructions and process standards for consistency in each production step. | Improved uniformity and quality control. |
| Continuous Improvement (Kaizen)4 | Encourages incremental, ongoing changes based on regular team feedback and performance data. | Sustained performance gains and waste reduction. |
| Equipment Upgrades & Automation | Invests in high-precision, automated equipment to reduce human error and variability, especially for pressing. | Increased productivity and reduced cycle time. |
| Cross-Training Employees | Ensures staff are proficient in multiple processes and understand lean principles to spot inefficiencies early. | Flexible workforce; reduces downtime and rework. |
| Rigorous Quality Control | Implements stringent quality checks at each critical stage, especially after complex processes like thermoforming. | Higher product quality; customer satisfaction. |
By executing these strategies, factories can optimize the combination of production techniques and materials, achieving a balance between cost reduction and performance enhancement.
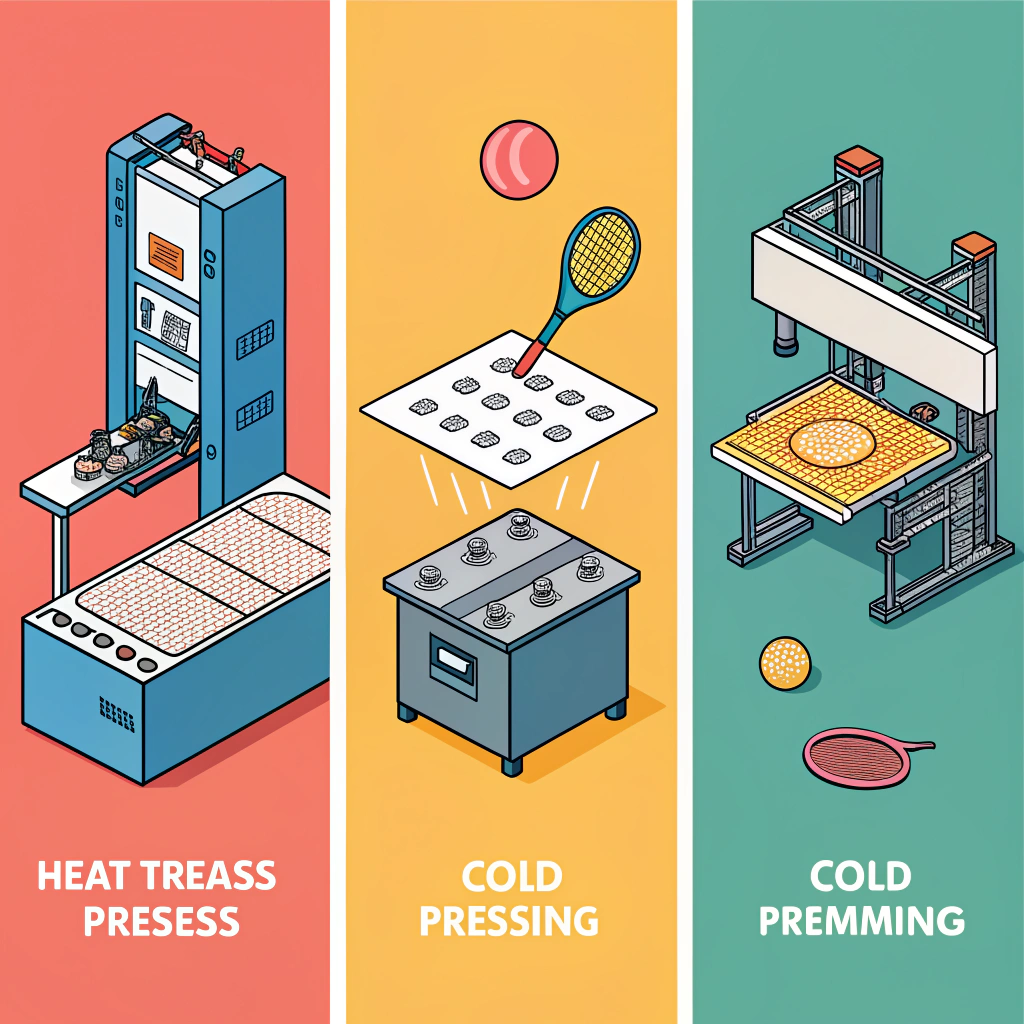
Production Process Optimization: Hot Pressing, Cold Pressing, and Thermoforming5
Each production method used in pickleball paddle manufacturing has distinct characteristics:
Hot pressing involves applying both heat and pressure to bond the layers and form the paddle.
Advantages:
- High production efficiency suitable for large-scale manufacturing.
- Produces strong and durable paddle surfaces with excellent impact resistance.
- Ensures structural integrity even in high-performance paddles.
Drawbacks:
- High initial investment in specialized equipment.
- The heat may slightly alter intrinsic material properties, potentially affecting the tactile feel of the paddle during play.
Cold pressing shapes the paddle materials at room temperature using mechanical pressure without heating.
Advantages:
- Greater control over paddle thickness and structural precision.
- Retains the original material properties, yielding superior ball feel and control.
- Ideal for designs that require high accuracy and consistency.
Drawbacks:
- Production cycles are longer compared to hot pressing.
- Requires precise pressure control and high-quality machinery, which may slow down overall throughput.
Thermoforming involves heating the material until it softens, then using molds to achieve complex paddle designs.
Advantages:
- Suitable for creating intricate designs and achieving exact material distribution.
- Maintains paddle stability and provides excellent design flexibility.
- Best suited for premium, custom-made paddle lines.
Drawbacks:
- Longer production time and higher equipment costs.
- Requires careful control of temperature and timing, which can complicate mass production.
A detailed comparison table further illustrates these differences:
| Process | Advantages | Disadvantages | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot Pressing | High efficiency, robust paddle structure, suitable for large-scale production | High equipment cost, potential material alteration | Standard high-performance paddles |
| Cold Pressing | Precise control, preserves material properties, enhanced paddle feel | Longer cycle time, demands precision equipment | Products requiring superior ball feel |
| Thermoforming | Complex shapes, precise material distribution, ideal for premium designs | Extended production time, higher costs | Customized, high-end paddle series |
Each of these methods has its place in a well-optimized production line. By aligning process selection with product requirements and lean strategies, manufacturers can significantly enhance operational performance.
One facility integrated lean production practices into its pickleball paddle manufacturing process with impressive outcomes. The plant began by mapping its entire production process to pinpoint inefficiencies. Specific measures included:
• Streamlining the mix of production techniques to match core materials with appropriate processes.
• Upgrading to automated systems for cold pressing, reducing cycle times by 15%.
• Implementing continuous improvement teams that met weekly to evaluate performance data.
These changes led to a 20% reduction in waste and a 10% overall boost in production efficiency while maintaining excellent quality control. The successful application of lean principles in this case demonstrates the importance of:
• Detailed process mapping to visualize bottlenecks.
• Strategic investment in automation and state-of-the-art machinery.
• A culture of continuous improvement that empowers team members to innovate from within.
The experience underscores that lean production is not a one-time fix but a continuous evolution aimed at operational excellence.
Waste reduction is a core principle of lean production. By eliminating non-value-added activities, factories can select cost-effective materials and reduce overproduction. Some practical steps include:
• Optimized Material Usage: By improving the matching of composite materials (e.g., carbon fiber versus fiberglass), manufacturers can reduce excess scrap and rework.
• Energy Efficiency: Upgrading machinery for better energy consumption helps reduce operational costs, translating into cost savings that can be redirected to quality improvements.
• Regular Audits: Implementing scheduled audits of both the production process and supply chain ensures that any deviations are swiftly addressed, maintaining high-quality standards across batches.
Robust quality control mechanisms, such as in-line inspections and post-production testing, ensure that every paddle meets the rigorous performance demands expected by competitive players. Integrating these measures with lean production strategies not only improves product quality but also significantly reduces operational costs over time.
For production managers and process engineers ready to implement lean production techniques in their pickleball paddle plants, consider taking the following steps:
- Conduct a comprehensive value stream mapping exercise to identify inefficiencies in each production process.
- Develop standardized work procedures for every stage—from material handling and pressing techniques to final quality inspections.
- Invest in training programs focused on lean principles for all operational staff, ensuring everyone shares a common goal of continuous improvement.
- Evaluate the feasibility of automation in high-variability areas such as cold pressing and thermoforming, balancing cost against potential efficiency gains.
- Establish regular performance audits to continuously monitor key metrics like waste reduction, cycle times, and defect rates.
- Leverage pilot projects in select production lines before a full-scale rollout to determine best practices and adjust as needed.
Integrating these steps into your operational strategy can create a sustainable framework for lean production that not only boosts efficiency but also positions your factory as a leader in pickleball manufacturing.
Adapting lean production approaches in pickleball manufacturing is a transformative journey that requires a deep understanding of both material science and process engineering. By focusing on eliminating waste, standardizing work procedures, and investing in modern automation, manufacturers can significantly improve operational efficiency while maintaining strict quality control. Lean methodologies provide the flexibility needed to adjust production processes as market demands evolve—making them an indispensable strategy in the competitive world of high-performance pickleball paddles.
For production managers, operations directors, and process engineers, the actionable strategies detailed in this article offer a roadmap to enhanced productivity and cost reduction. Now is the time to re-evaluate your production processes, identify inefficiencies, and implement lean solutions that will lead your facility toward operational excellence and sustainable growth.
Q: How is a pickleball paddle made?
A: A pickleball paddle is typically manufactured using a layered sandwich structure. The paddle comprises a honeycomb core that is laminated with surface materials. These layers are selected based on compatibility and performance criteria. Techniques such as hot pressing, cold pressing, and thermoforming are used to bond the layers together, ensuring a balanced combination of strength, durability, and desired tactile properties.
Q: What is the history of Selkirk pickleball?
A: Selkirk Sport was founded in 2014 by the Barnes family, marking its entry into the competitive arena of pickleball paddle manufacturing. Since its inception with models like the 200A and 300A, Selkirk has grown into a recognized premium brand, known for innovative design and high-quality products that have influenced industry standards.
Q: How many pickleball manufacturers are there?
A: As of 2024, there are approximately 897 pickleball paddle manufacturers worldwide. This figure reflects the global expansion of the sport and the growing number of companies dedicated to producing approved, high-performance pickleball paddles.
-
Lean production: Click to read an in-depth exploration of lean production methods for reducing waste and streamlining manufacturing processes, helping you implement efficient operational strategies. ↩ ↩
-
Value Stream Mapping: Click to learn more about mapping your production process to identify non-value-added steps, uncover bottlenecks, and improve overall efficiency. ↩ ↩
-
Standardized Work Procedures: Click to understand the importance of creating and maintaining standardized work procedures for ensuring consistency and quality in production processes. ↩ ↩
-
Continuous Improvement (Kaizen): Click to explore the principles of continuous improvement (Kaizen), and how incremental changes can drive long-term operational excellence. ↩ ↩
-
Thermoforming: Click to discover the thermoforming process, including its advantages in producing complex shapes and considerations for cost and production time. ↩ ↩