In today’s competitive sports equipment market, making the right choice for pickleball paddle construction1 is essential. Manufacturers and procurement specialists must evaluate a variety of materials and production processes to ensure that the chosen paddles deliver superior performance, unmatched durability, and consistent quality. This article provides a quick overview and a detailed side-by-side comparison of different manufacturing methods based on pickleball paddle construction techniques such as carbon fiber (3K, 12K, T300 carbon fiber2), fiberglass, composite materials, and various core technologies combined with production processes like hot pressing, cold pressing, and thermoforming.
The performance and cost-effectiveness of a pickleball paddle rely on two major aspects: material composition and manufacturing process. In our comparison, we break down these elements to help you understand which combination will best meet your business needs.
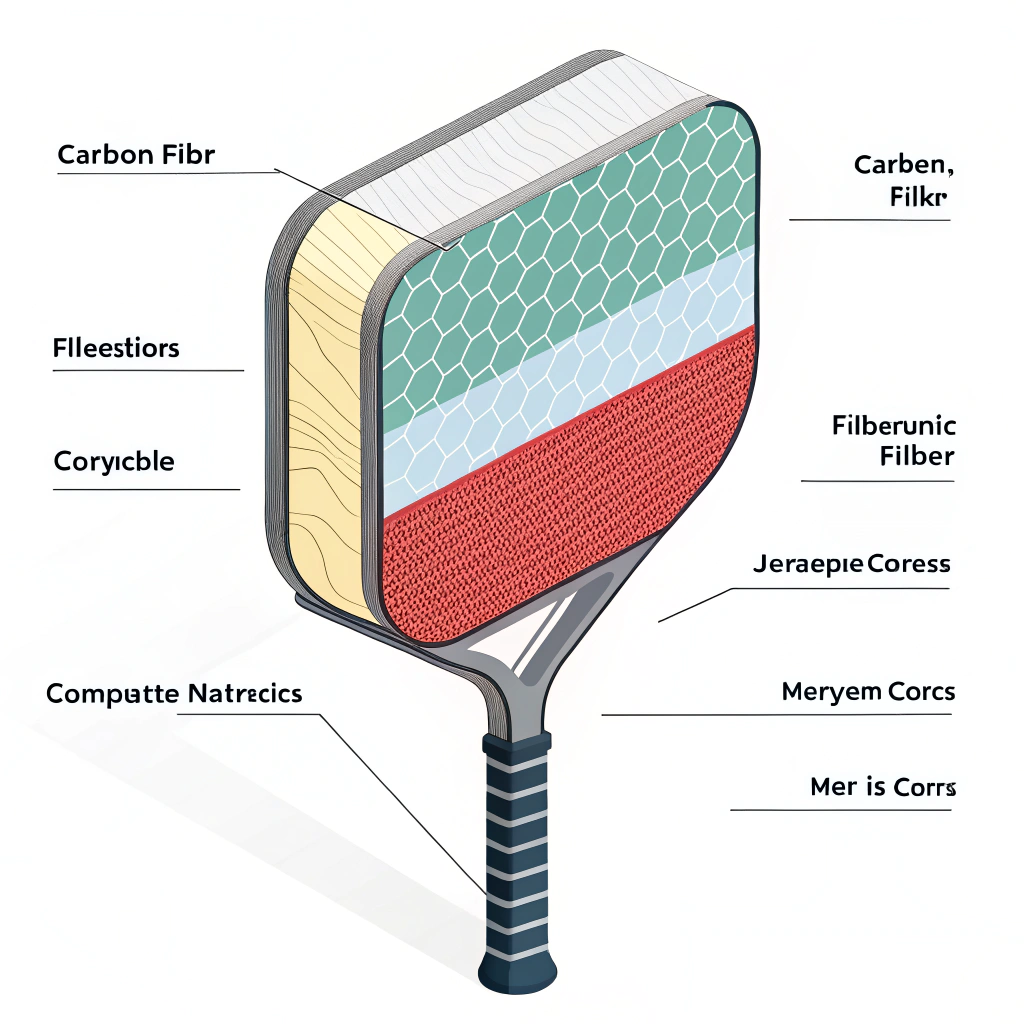
Pickleball paddles constructed from high-performance materials deliver specific advantages. Below is an analysis of the primary materials used in paddle construction:
- 3K Carbon Fiber:
Known for its excellent strength and flexibility, 3K carbon fiber offers high rebound force and reduces vibration during play. This material is ideal for players who require durability and a responsive hitting experience. - 12K Carbon Fiber:
With a higher thread density, 12K carbon fiber provides a smoother surface, enhanced hardness, and increased impact resistance. It is best suited for competitive players needing both power and longevity. - T300 carbon fiber2:
A high-performance option renowned for its superior tensile strength, T300 carbon fiber presents a balanced combination of strength and lightweight feel, making it a favorite among players who demand precision.
- E-Glass Fiberglass:
Fiberglass paddles, particularly those made with E-Glass, offer a good balance between power and control. They have a more extensive sweet spot and are known for their flexibility, allowing for excellent ball control even in intense play.
- Carbon Fiber and Fiberglass Composite:
This composite takes advantage of the strengths of both carbon fiber and fiberglass. The blend results in paddles that are strong, light, and flexible, providing an ideal balance for versatile play styles. - Bamboo Core Composite:
Bamboo cores are prized for being lightweight and highly impact resistant, providing a distinct hitting feel that many recreational and competitive players appreciate. - Honeycomb Core:
Typically made from high-density polymer or pulp, the honeycomb structure absorbs shock effectively, reducing unwanted vibrations and extending the paddle’s lifespan.
- Nomex Honeycomb Core3:
Offering remarkable shock absorption and durability, Nomex cores are considered ideal for players seeking long-lasting stability and improved ball response. - Aluminum Honeycomb Core:
Aluminum cores ensure a balanced weight distribution, contributing to both power and precision during play. - Polymer Honeycomb Core:
These cores provide excellent elasticity and improved comfort, thereby reducing vibration and offering an enhanced touch on the ball.
Manufacturing Processes: Hot Pressing, Cold Pressing, and Thermoforming4
The manufacturing process plays a crucial role in defining the final characteristics of the paddle. Each process offers its own set of advantages and limitations:
Hot pressing involves heating materials and applying significant pressure to mold the paddle.
- Advantages:
• Achieves high production efficiency suitable for large-scale manufacturing.
• Results in strong paddles with excellent resistance to impact.
• Ensures robust structural integrity. - Disadvantages:
• May alter the intrinsic properties of the materials, potentially affecting the paddle’s feel.
• Requires considerable investment in specialized equipment.
Cold pressing reshapes materials at room temperature using mechanical pressure, delivering precise control over paddle thickness and design.
- Advantages:
• Maintains the natural properties of the materials, ensuring better ball feel and responsiveness.
• Enables precise control over the paddle’s structural features. - Disadvantages:
• Has a longer production cycle, which might limit manufacturing throughput.
• Demands high-precision equipment to ensure consistent quality.
Thermoforming involves heating materials to a point where they soften, then molding them into the desired shape using custom-designed molds.
- Advantages:
• Allows for the production of paddles with intricate designs and a well-distributed material layout.
• Enhances paddle stability, thereby further improving performance. - Disadvantages:
• Typically more time-consuming than other methods.
• Requires advanced and costly equipment, making it more viable for premium, high-performance products.
For decision-makers, a clear understanding of the trade-offs between materials and production techniques is crucial. The table below summarizes the key differences and benefits:
| Category | Material/Process | Advantages | Disadvantages | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Fiber | 3K, 12K, T300 | High strength, durability, and reduced vibration | Variability in stiffness and feel depending on thread density | Competitive play, high-performance paddles |
| Fiberglass | E-Glass | Excellent ball control, broader sweet spot | Less rigid than carbon fiber, may not deliver the maximum power | Recreational players, balanced performance |
| Composite | Carbon/Fiberglass, Bamboo Core Composite | Offers balance between weight, strength, and flexibility | May have higher production costs | Custom and versatile play styles |
| Core Materials | Nomex, Aluminum, Polymer Honeycomb cores | Varies from enhanced shock absorption (Nomex) to balanced weight (Aluminum) | Trade-offs in terms of elasticity and vibration reduction across types | Varies based on playing needs |
| Hot Pressing | Production Technique | Fast production rate, robust paddle structure | Requires high investment, may compromise material’s natural feel | Large-scale manufacturing, competition use |
| Cold Pressing | Production Technique | Precise control, better preservation of material integrity | Slower production cycle | Premium paddles with exacting standards |
| Thermoforming | Production Technique | Allows complex designs, precise material distribution | Longer cycle times, high equipment cost | High-performance, custom-engineered paddles |
This comprehensive table can guide your purchasing decision by highlighting the key metrics that matter in performance and cost. By having a clear comparison, you are better able to align product offerings with client expectations and competitive market standards.
Choosing the right combination of materials and production processes is not only about performance but also about cost, durability, and production efficiency. Here are some considerations:
-
Cost versus Performance:
Higher-performance materials like T300 carbon fiber2 or advanced composite structures often come with increased costs. When targeting high-end markets or professional players, the increased expense can be justified by the superior performance and durability. In contrast, fiberglass-based paddles, while offering less power, provide a more balanced cost-to-performance ratio suitable for recreational players. -
Production Efficiency:
Hot pressing generally allows for faster production, which is beneficial for large-volume orders. However, when precision and paddle feel are prioritized, Cold Pressing5 might be preferred despite its longer cycle times. Manufacturers must weigh the benefits of rapid output against potential compromises in tactile performance. -
Durability and Comfort:
The right core material can significantly impact the paddle's lifespan and player comfort. For example, Nomex Honeycomb Core3 provides excellent shock absorption for aggressive players, while polymer cores focus on reducing vibration, thereby creating a softer, more comfortable experience for beginners. -
Customization and Market Differentiation:
With the increasing demand for personalized sports equipment, the ability to customize paddle designs is a considerable advantage. Processes like thermoforming allow manufacturers to create paddles with unique shapes and intricate design details that not only cater to player preferences but also help differentiate a brand in a crowded market.
When deciding on the manufacturing process and material composition for your next order of pickleball paddles, consider the following action points:
-
Evaluate Your Target Market:
Determine whether your customers prioritize raw performance, durability, or cost-efficiency. For high-level competition, invest in premium materials like T300 carbon fiber2 and cold pressing techniques. For broad-market appeal, fiberglass or composite options with hot pressing might be more appropriate. -
Analyze Production Capacities:
If rapid scale-up is critical, hot pressing may provide the necessary output. However, if quality is the main concern, consider the benefits of Cold Pressing5 despite its slower pace. -
Balance Material Trade-offs:
Use our comparative table to align each material’s advantages with specific performance criteria. For instance, if low vibration is crucial, prioritize polymer cores and E-Glass fiberglass. Meanwhile, if maximum power is desired, switch to 12K carbon fiber or aluminum honeycomb cores. -
Consider Customization Options:
Leverage the flexibility of thermoforming to accommodate custom orders. This can be a key differentiator when catering to niche markets or individual teams seeking branded equipment. -
Test and Validate:
Before committing to large production runs, consider a small batch trial to validate your paddle performance against the intended usage scenarios. This approach minimizes risks and ensures that the final product meets stringent quality standards.
In an industry where equipment quality directly influences competitive performance and player experience, understanding the nuances of pickleball paddle construction1 is paramount. By carefully evaluating both the material options—ranging from various carbon fibers to innovative composites—and the manufacturing techniques available, you can make informed decisions that balance cost, efficiency, and high performance.
This detailed comparison serves as a guide for product managers and procurement specialists to strategically choose the best combination that meets their market demands, thereby ensuring both customer satisfaction and competitive edge.
People Also Ask
Q: What are the best pickleball paddles made from?
A: The best pickleball paddles are typically made from premium materials like carbon fiber (including variants such as 3K, 12K, and T300), fiberglass, and composite materials. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize excellent handling and feel or increased power and durability.
Q: What is the difference between T700 and T800 pickleball paddles?
A: T800 raw carbon fiber paddles offer about 20% higher tensile and fatigue strength compared to T700, resulting in more powerful shots and a longer lifespan under high-intensity play conditions.
Q: How are pickleball paddles constructed?
A: Most pickleball paddles are constructed using a sandwich method, where the core material—such as nomex, aluminum, or polymer honeycomb—acts as the center, with durable face materials on both sides, providing a consistent blend of power, control, and durability.
-
pickleball paddle construction: Read more to understand the critical aspects and design approaches behind building high-performance pickleball paddles that meet market standards. ↩ ↩ ↩2
-
T300 carbon fiber: Read more to explore the properties of T300 carbon fiber, including its tensile strength and lightweight characteristics that contribute to elite paddle performance. ↩ ↩ ↩2 ↩3 ↩4
-
Nomex Honeycomb Core: Read more to understand how Nomex honeycomb cores improve shock absorption and longevity in sports equipment through advanced material engineering. ↩ ↩ ↩2
-
Thermoforming: Read more to learn about the thermoforming process, its benefits in producing complex shapes and enhancing material distribution in manufacturing. ↩ ↩
-
Cold Pressing: Read more to discover how cold pressing maintains material integrity to ensure better ball feel and control in precision-engineered paddles. ↩ ↩ ↩2 ↩3