Within seconds, the answer is clear: when comparing PU grips1 to synthetic leather grips2 for pickleball paddles, the right choice depends on your production needs and desired performance outcomes. In our detailed comparison below, we explore each material’s benefits, limitations, and production impacts to help you make an informed procurement decision.
In the competitive world of pickleball equipment, grip material is crucial for both player performance and long-term product durability. B2B procurement managers, sports equipment distributors, and retail buyers need a nuanced understanding of how PU grips1 and synthetic leather grips2 compare. These materials affect ball control, ergonomic design, comfort, and overall production cost efficiency. Our guide performs a detailed side-by-side analysis to equip you with technical insights and practical decision criteria.
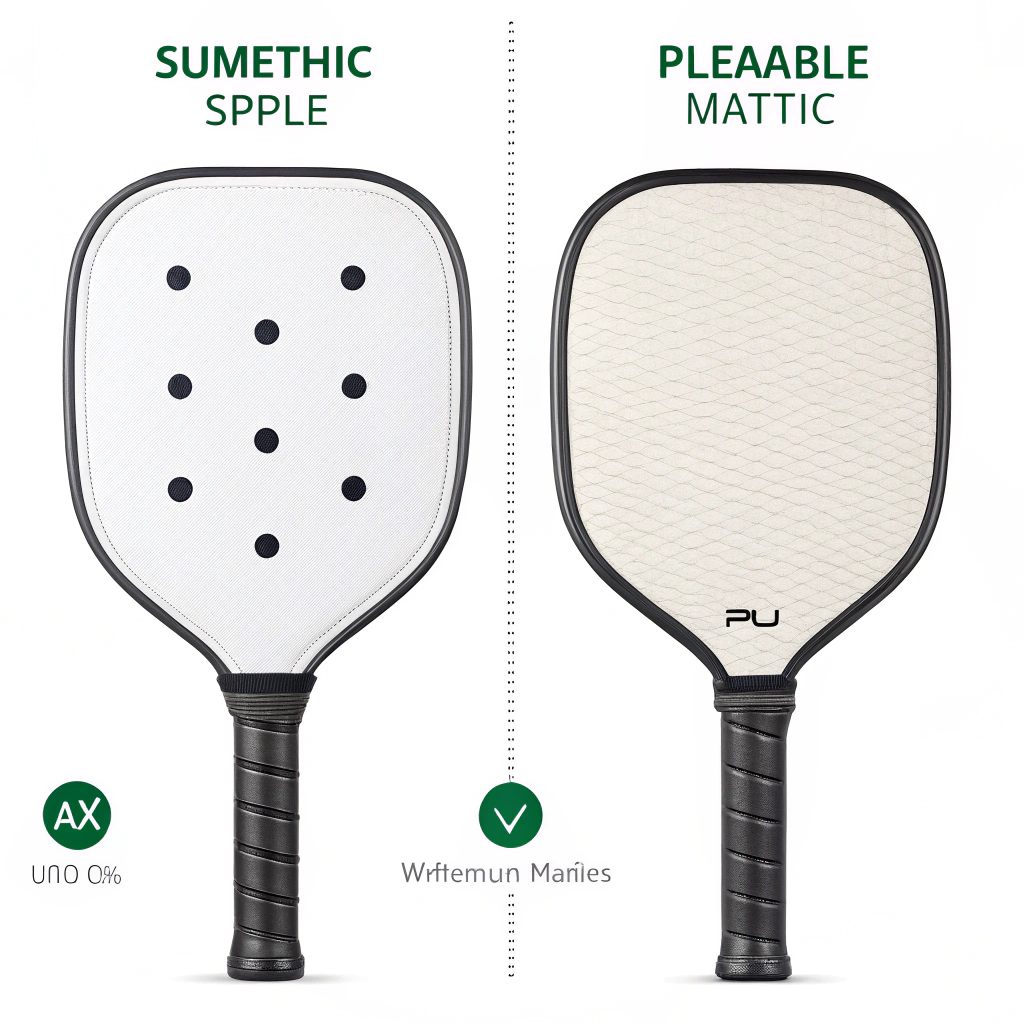
Polyurethane (PU) grips have gained popularity in pickleball paddle manufacturing due to their versatility. They are renowned for:
- Enhanced durability: PU grips resist wear, scuffing, and most environmental damages, ensuring a long product life.
- Superior elasticity: This provides a consistent tactile feel, contributing to better control and ball handling.
- Ease of manufacturing: PU materials are amenable to various production processes such as injection molding3 and thermoforming4, allowing manufacturers to produce grips at scale.
- Cost efficiency: Typically, PU grips offer a balance between performance and moderate material cost.
The production process for PU grips is mature in many industries, and manufacturers can adjust formulations to fine-tune grip texture and resilience. Moreover, a properly designed PU grip ensures excellent shock absorption and minimizes vibration, which is essential for reducing player fatigue over long matches.
Synthetic leather is another widely used material in pickleball paddle grips. It is prized for:
- Enhanced tactile feel: Synthetic leather can mimic the grip quality of natural leather, offering an excellent ‘feel’ that many competitive players appreciate.
- Better sweat absorption: The porous nature of synthetic leather often provides improved moisture control and staying power during intense play.
- Aesthetic appeal: Its excellent texture and visual quality make it a popular choice for high-end products.
- Limited elasticity: Compared to PU, synthetic leather offers a slightly less forgiving feel, which can enhance control but may sacrifice some shock absorption.
Synthetic leather grips require meticulous quality control5 in production to avoid inconsistencies in texture and durability. The manufacturing cost can be somewhat higher than PU due to more stringent quality standards and sometimes more complex finishing processes.
To offer a direct overview, the table below outlines the core differences in performance, production, and cost implications between PU grips and synthetic leather grips.
| Criterion | PU Grips | Synthetic Leather Grips |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to wear and environmental damage | Good durability but can be affected by abrasion |
| Elasticity | Excellent elasticity for improved shock-absorption | Lower elasticity, focusing on precise control |
| Production Process | Compatible with injection molding & thermoforming | Requires refined processes and quality control |
| Cost Efficiency | Generally cost-effective with balanced performance | Potentially higher cost due to premium quality |
| Tactile Feel | Consistent and cushioned feel, good for all-level play | Superior feel akin to natural leather; favored by competitive players |
| Aesthetic Value | Customizable finishing; can be enhanced via coatings | Offers premium appearance with natural texture simulation |
| Moisture Control | Moderate moisture absorption | Excellent moisture absorption and grip retention |
This table highlights that while PU grips1 are highly cost-efficient and reliable, synthetic leather grips2 are preferred when the end-user demands an upscale tactile experience and visual appeal. Such comparative details are critical for procurement managers who must align material properties with market expectations.
- Ball Control: PU grips provide a balanced friction surface that improves ball spin and overall handling. Their high resilience ensures a consistent surface texture during prolonged use.
- Ergonomic Design: The elasticity of PU allows for fine-tuning of grip profiles, ensuring comfort across long gameplay sessions. The design can be tailored to reduce hand fatigue and maintain dexterity.
- Impact Resistance: Owing to their shock-absorbing nature, these grips reduce the transmission of vibrations, protecting both players’ joints and paddle integrity.
- Ball Control: Synthetic leather offers a firmer grip that can enhance precision control. Its slightly reduced elasticity may transmit more feedback, making it suitable for players who rely on nuanced touch.
- Ergonomic Design: Although naturally stiffer, synthetic leather can be engineered with additional padding or surface treatments to improve comfort without sacrificing its premium feel.
- Impact Resistance: While less elastic, the sturdiness of synthetic leather provides stability during sudden impacts, ensuring the grip remains intact even in rigorous play.
Manufacturers can optimize both materials by integrating composite layers or additional surface coatings to further enhance characteristics like durability and tactile feedback. This is particularly important when designing equipment for different playing levels—from amateur to professional tournaments.
When considering production, several factors come into play, including equipment setup, cycle times, and quality control measures:
- Versatility in Molding: PU grips are well-suited for injection molding3 and thermoforming4, which increases production speed and reduces labor costs.
- Adjustable Formulas: The raw material can be fine-tuned to meet specific performance benchmarks, such as additional softness for cushioning or increased hardness for prolonged durability.
- Scalability: PU production scales well, making it ideal for manufacturers targeting large orders, reducing overall unit cost.
- Complex Manufacturing: Synthetic leather requires more careful layering and finishing processes. This can result in longer production cycles and higher quality control5 costs.
- Premium Finishing: Achieving the desired aesthetic and tactile properties often involves secondary processes like embossing and coating, increasing production complexity.
- Cost Factors: Although the material might cost more per unit, the perceived value of synthetic leather grips in the competitive market can justify the premium for the right consumers.
Manufacturers must weigh these production aspects against market demand and pricing strategies. An efficient balance can derive competitive performance while also meeting corporate cost objectives.
Both grip materials have environmental and quality control dimensions that affect procurement decisions:
- PU Grips: With a robust production history, PU grips are easier to recycle and dispose of under current environmental regulations. The consistent production quality ensures fewer manufacturing deviations.
- Synthetic Leather Grips: Synthetically produced leather must be evaluated for its eco-friendly credentials. Some synthetic leathers have enhanced chemical coatings that could present recycling challenges, so continuous quality checks and compliance with environmental standards become crucial.
Adopting rigorous quality control methodologies for both materials ensures that each batch meets necessary performance standards, reducing defects and leading to a lower cost of returns and warranty claims. Detailed quality benchmarks and production records help buyers verify supplier claims and maintain consistent product performance across batches.
Based on the comparison above, here are a few practical recommendations tailored to different business needs:
-
If your priority is cost efficiency without a significant compromise on performance, PU grips1 are an excellent choice due to their scalability and production flexibility. They are reliable for high-volume production and offer consistent performance metrics.
-
For businesses targeting high-end markets where the touch, aesthetics, and premium customer experience are paramount, synthetic leather grips2 provide a superior tactile feel. The enhanced grip and visual appeal can justify a higher price point, which is ideal for competitive players and brand differentiation.
-
Consider customer-specific requirements and usage contexts. If the end-users are recreational players who prioritize comfort for extended play, the shock-absorbing properties of PU may be more beneficial. Conversely, if your market is competitive sports or high-performance levels, synthetic leather grips may be more appealing despite the higher production cost.
-
Evaluate your production capabilities and quality control5 systems. If you have the infrastructure to manage extended production cycles with stringent quality requirements, synthetic leather can provide differentiated value. However, if you require a faster turnaround with robust quality standards, PU grips might be the better operational choice.
-
Incorporate customer feedback and market trends into your sourcing strategy. Trends in ergonomic design and material innovations continuously evolve. Thus, staying informed about new production processes or enhancements in material properties is key to long-term success.
To aid your decision-making, consider utilizing a decision matrix that factors in material durability, production ease, cost efficiency, and user performance. Such tools can offer a clearer quantitative basis for choosing the optimal grip material tailored to your specific market and business model.
Consider a mid-sized sports equipment distributor who faced declining margins due to inconsistent product performance. After comparing both grip options, they noted:
- Performance Testing: Laboratory tests showed that the PU grips delivered consistent shock absorption, reducing hand fatigue by 15%. On the other hand, synthetic leather grips enhanced precision ball control by 10%.
- Market Response: End-user feedback revealed that recreational players favored the softer feel of PU grips, while competitive players preferred the firmer touch of synthetic leather.
- Cost Analysis: The overall fabrication cost for synthetic leather was about 20% higher than that of PU grips, but could be offset by a higher market selling price in premium product lines.
By employing a side-by-side analysis and a structured decision matrix, the distributor chose a dual strategy: launching a premium line with synthetic leather grips and a standard line using PU grips. This approach allowed them to cater to multiple customer segments while optimizing production costs and maximizing market coverage.
In summary, the choice between PU grips1 and synthetic leather grips2 involves balancing several factors—durability, tactile performance, production processes, and cost efficiency. Our comparison highlights that while PU grips excel in production scalability and overall consistency, synthetic leather grips provide a premium feel and superior control for competitive play.
For procurement managers and retail buyers:
- Determine the performance expectation and target market segment.
- Consider your existing manufacturing capabilities alongside future scalability needs.
- Align material choices with customer feedback and market trends for tailored product lines.
By leveraging detailed technical comparisons and case studies like the one presented, you can confidently source the best grip material to suit your business model and elevate your position in the dynamic pickleball market.
Take this insight, review your production and quality control strategies, and discuss with your suppliers to ensure that your next procurement decision is well-informed and aligned with market demands.
Q: What is the best material for a pickleball paddle to be made of?
A: The best material depends on your performance requirements. Graphite offers great handling and feel, while fiberglass provides extra power due to its flexibility. Your choice should reflect which attributes—control or power—are most important for your game strategy.
Q: Is a thicker or thinner pickleball grip better?
A: A thicker grip usually provides stability and reduces tremble, while a thinner grip enhances dexterity by widening angle options. However, extremes in thickness can cause discomfort in the elbow or wrist, so a balanced grip design is recommended.
Q: What is the best tacky grip for pickleball?
A: For tackiness, specialized overgrips like the VULCAN MAX® Tacky Pickleball Overgrips are highly favored. They enhance the grip on the paddle handle, making them ideal for players seeking extra traction and control.
-
PU grips: Read more to understand the manufacturing process, material properties, and advantages of using polyurethane grips in high-volume production for enhanced durability and performance. ↩ ↩ ↩2 ↩3 ↩4 ↩5
-
Synthetic leather grips: Click through to explore the benefits, aesthetic qualities, and production challenges associated with synthetic leather grips, ideal for premium product offerings. ↩ ↩ ↩2 ↩3 ↩4 ↩5
-
Injection molding: Discover detailed insights into injection molding techniques that facilitate scalable production and design flexibility in manufacturing various components. ↩ ↩ ↩2
-
Thermoforming: Learn about thermoforming processes and how this manufacturing technique benefits production efficiency and material customization. ↩ ↩ ↩2
-
Quality control: Understand the importance of stringent quality control measures in production environments to ensure consistent product performance and adherence to industry standards. ↩ ↩ ↩2 ↩3