HS codes are the backbone of international trade compliance1, ensuring that high-performance pickleball products are classified correctly for smooth customs clearance2 and accurate tariff calculations3. In this article, we explain the importance of HS codes4 in the pickleball industry, explore the complexities of classifying products like paddles and accessories, and provide practical guidance and examples for determining the right classification.
HS codes, or Harmonized System codes, are internationally standardized numbers used for classifying traded products. They facilitate customs procedures and ensure that each product is categorized accurately for tariff assessment. For businesses like NEX Pickleball, this classification is critical not only for regulatory compliance but also for cost control and efficient export/import operations.
Why HS Codes Matter:
• They simplify international shipments by providing a common language between customs authorities around the world.
• They help in determining the applicable tariffs and trade agreements for high-performance sports equipment.
• A correct HS code assignment reduces delays at customs and avoids misclassification penalties.
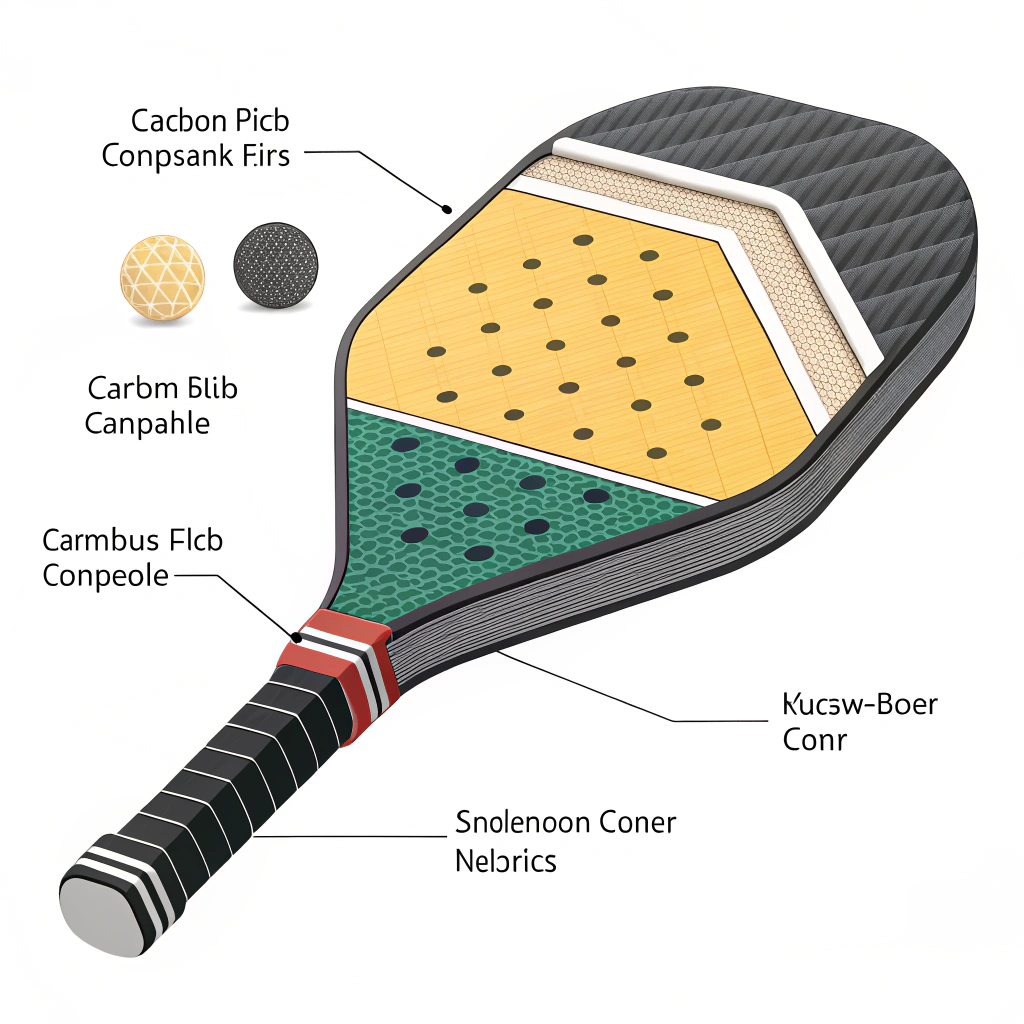
The primary challenge for trade compliance managers and export/import professionals is accurately classifying complex products that incorporate advanced materials and production techniques. High-performance pickleball products, like paddles made from 3K, 12K, and T300 carbon fiber, as well as composite and honeycomb core constructions, can easily straddle multiple HS code categories. The key problems include:
• Identifying the correct HS code for each component (paddle, ball, overgrip, etc.).
• Dealing with variations in material composition, such as the differences between fiberglass, carbon fiber, and composite materials.
• Navigating through regulatory differences across international borders.
• Balancing the technical properties of the product with the statutory requirements outlined by customs agencies.
Several factors drive the classification complexities:
-
Material Variety:
- High-performance pickleball accessories are made of diverse materials. For example, paddles may feature 3K Carbon Fiber for strength and flexibility or Aluminum Honeycomb Cores for a balance of precision and durability.
- Each material has its own set of properties that may suggest different tariff codes even if the final product category appears similar.
-
Production Processes:
- Techniques such as hot pressing, cold pressing, and thermoforming influence the tactile feel and performance of the paddles.
- These processes may affect how customs classify the product based on its physical characteristics and manufacturing method.
-
Product Complexity:
- Accessories surrounding the pickleball game—such as the ball, overgrip, wristbands, and even custom branding elements—create overlapping classifications.
- Differences in intended use (recreational vs. competitive) can also influence HS code assignment.
To navigate the complexities of classifying high-performance pickleball products, consider the following structured approach:
The HS Code system is organized into chapters and headings that group products based on shared characteristics. For pickleball products:
- Paddles: Often fall into categories related to sporting goods or wooden/composite articles.
- Balls and Accessories: May be classified under sections for sports equipment or specific articles based on material composition.
Key Tip: Always start by reviewing the specific material composition and usage of the product. For instance, a paddle made primarily of carbon fiber could be classified differently from one with a wooden core.
Break down your product into major components:
| Component | Material(s) Used | Considerations for HS Code |
|---|---|---|
| Pickleball Paddle | 3K/12K/T300 Carbon Fiber, Composite | Evaluate the dominant material and manufacturing process |
| Core | Nomex/Aluminum/Polymer Honeycomb | Focus on impact absorption and rigidity introduced by the core |
| Additional Accessories | Overgrips (rubber or foam), Wristbands | Different materials may fall under separate sports equipment categories |
Note: In many cases, the primary HS code is determined by the paddle’s overall structure and performance characteristics rather than by each individual material.
- Regulatory Resources: In many countries, the customs website provides detailed tariff classification guidelines that can help verify which HS codes apply.
- Industry Standards: Align your product descriptions with industry-accepted terms as used in the Harmonized System.
Action Step: Maintain an updated database of HS code assignments related to your products and regularly review any changes in local guidelines.
For complex products, it’s often wise to seek advice from trade consultants who specialize in customs classification. Their expertise can be especially valuable when product materials and manufacturing techniques evolve rapidly.
Practical Tip: Consider periodic training sessions for your compliance team on HS code updates to ensure you remain aligned with international practices.
- Internal Audits: Regularly audit your HS code categorization process as part of your quality control systems.
- Software Solutions: Implement trade compliance software5 that updates HS code modifications and integrates feedback from customs authorities if discrepancies occur.
Understanding the classification for each pickleball product is essential. Below are insights into some common items:
Given the importance of materials in determining performance, pickleball paddles often face scrutiny under several HS code subheadings. For instance:
- HS Classification Factors:
• The material type (e.g., carbon fiber versus composite)
• Manufacturing technique (e.g., hot pressing may denote a certain level of durability and impact resistance)
• Intended use (recreational versus professional competitive settings)
In practice, a high-performance paddle geared towards competitive play might be aligned with categories typically reserved for specialized sporting equipment due to its enhanced features and premium materials.
Other items, like overgrips and wristbands, should be classified separately if they do not form part of the main paddle assembly. Their HS codes may be entirely different from the primary product line:
- Overgrips and Wristbands: Look into textile or rubber article classifications that apply.
- Patchwork on Paddles: If custom branding additional to the paddle’s primary construction, verify if they alter the overall classification.
Below is a consolidated table for quick reference to guide HS code assignments based on common pickleball product attributes:
| Product Component | Recommended HS Code (Example) | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Pickleball Paddle | Varies (Refer to Section 95*) | Material dominant factor; carbon fiber vs. composite |
| Pickleball Ball | 9506590000 | Typically classified under sporting goods |
| Overgrips/Wristbands | 9506919000 | Often fall under accessory categories for sports gear |
| Custom Branding Elements | Varies | Depends on material and integration with the primary item |
*Note: HS codes may differ by jurisdiction. Always confirm with local customs guidelines.
When applying HS codes for high-performance pickleball products, it is important to consider:
• Material Evolution: As technology advances, new materials may emerge, requiring updated classifications.
• Jurisdictional Variations: HS codes are generally harmonized but may have regional modifications.
• Documentation Quality: Accurate documentation of manufacturing processes and materials used is essential for compliance.
• Training and Audit Requirements: Ongoing compliance training for your team minimizes errors in classification and customs documentation.
Limitation: While tables and guidelines provide a good starting point, the final classification often requires consultation with customs or a trade specialist, especially when complex composite materials are involved.
Accurate HS code classification is a critical element in ensuring smooth international trade operations for high-performance pickleball products. The process demands a clear understanding of the product’s material composition, the production process, and regulatory requirements across various jurisdictions.
Actionable recommendations include:
- Conducting regular reviews and audits of HS code assignments.
- Collaborating with trade compliance experts or consultants.
- Investing in trade compliance software that integrates ongoing changes in classification standards.
- Documenting and standardizing your manufacturing processes for accurate classification and smoother customs clearance.
By following these best practices, companies like NEX Pickleball can ensure that each product is classified correctly, reducing the risk of customs delays and minimizing classification errors that could lead to additional tariff burdens. This not only streamlines logistics but also builds credibility with international trade regulators.
• What is the HS code for pickleball?
HS codes for pickleball products vary by component; for instance, some vendors interpret specific codes (such as HS code 5201) for pickleball items. However, it is crucial to review the exact material composition and manufacturing process to assign the correct classification.
• What is the HS code for paddles?
While HS Code 44219188 has been referenced for canoe paddles, high-performance pickleball paddles typically require a different classification considering their composite construction and advanced materials. The code can vary depending on materials like carbon fiber and the production method used.
• What is the HSN code for pickleball paddle?
For pickleball paddles, some industry references mention categories under HS:9506590000 for pickleball balls and related equipment, while other accessories like paddle overgrips might fall under HS:9506919000. The exact HSN code depends on the specific product features and material composition.
-
Trade compliance: Click to explore the strategies and regulatory frameworks that ensure companies adhere to international trade laws and maintain smooth cross-border operations. ↩ ↩
-
Customs clearance: Click to understand the processes and requirements for moving goods across international borders without delay. ↩ ↩
-
Tariff calculations: Click to discover how tariffs are determined based on product classifications and the impact on overall trade costs. ↩ ↩
-
HS codes: Click to learn how internationally standardized product classification systems help streamline customs operations and set tariffs based on detailed product characteristics. ↩ ↩
-
Trade compliance software: Click to delve into technological solutions that automate and optimize regulatory compliance processes for international trade. ↩ ↩